Overview¶
Physical networks¶
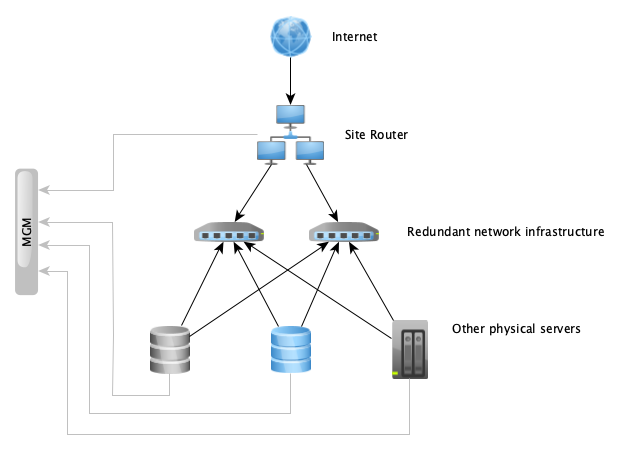
We use a redundant routed layer 3 network as the basis of production network functions in all our public datacenters. All of our servers in each location are connected to redundant network infrastructure, which forwards network traffic between the servers. This redundancy allows maintenance actions or failures of individual network devices without customer impact.
On top of this routed network we use an overlay technology called EVPN-VXLAN, which allows us to run multiple logically separate layer 2 or layer 3 networks over shared physical infrastructure. All of our logical networks aside from the out-of-band management network are implemented as virtual networks running through this overlay.
The management network uses separate physical infrastructure and is implemented as a simple flat layer 2 network using dedicated switches.
In all locations, the routed layer 3 network carrying production traffic uses links of at least 10G, which is available to all the virtual networks running on top of the overlay. In our public datacenter RZOB both routers each have 10G connectivity to our uplink provider. In WHQ our routers each have a 10G link to our uplink provider, however this provider only has non-redundant 3G connectivity itself.
The routers participate in the EVPN-VXLAN overlay, having access to the frontend network and server-to-server network, and are additionally connected to the management network.
Logical networks¶
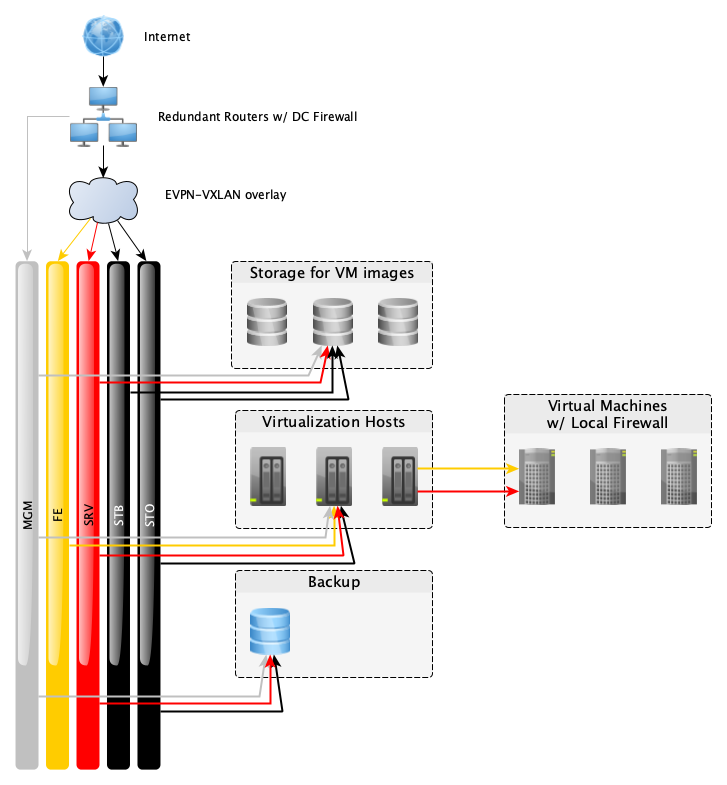
Our logical networks can be implemented as either layer 2 VLANs or virtual networks inside an EVPN-VXLAN overlay due to a unified internal numbering scheme. All networks use layer 2 transport unless otherwise noted. We have the following logical networks in use:
MGM - Management, purely for administrative purposes. This network connects switch management ports, baseband management controllers, and additional access to server OSes via SSH. Not accessible from the outside world, private IPv4 address space.
FE - Frontend, for customer application traffic. This network connects to managed machines that provide customers’ application to the public. This network is switched to the VM and leverages completely public traffic. The DC firewalls do not filter this, however the default system firewall running locally on managed VMs blocks inbound connections. Customer applications are free to use any ports they like. These ports must be listed in the firewall configuration in order to receive inbound connections. All managed VMs receive a NIC on this network but not necessarily IPv4 or IPv6 addresses if they do not provide public services. DNS example: vm00.fe.rzob.fcio.net.
SRV - Server to server communication. Used for customer application components running in managed VMs to talk to each other, e.g. database traffic and for management purposes on the application level. This network is firewalled from the internet at our DC edge firewalls and allows only HTTP(S) and SSH traffic. Additionally, managed VMs can filter this traffic locally, and only allow arbitrary traffic from VMs belonging to the same project by default. This network is used on all managed VMs and has IPv4 (usually private) and IPv6 addresses allocated automatically. DNS example: vm00.srv.rzob.fcio.net or simply vm00.fcio.net.
PUB - Public, for traffic to unmanaged VMs. Unmanaged VMs which are not running our managed platform receive a NIC on this network and public IPv4 and IPv6 addresses in order to provide general access to and from the internet. This network uses a layer 3 transport, and is not firewalled. Unmanaged VMs do not come with a preconfigured local firewall – if such a firewall is desired then customers must configure this themselves. DNS example: vm00.pub.rzob.fcio.net
STO - Storage communication. Used by the virtualization and backup servers to access the network storages where the VM disk images as well as object storage gateways (RadosGW) are located. DNS example: filer.sto.rzob.gocept.net.
STB - Storage backend communication. Used by the storage layer for replication and self-management. DNS example: filer.stb.rzob.gocept.net.
Individual VMs that run management services, like monitoring, may get bridged into additional networks or granted firewall exceptions as necessary.
The routers suppress “martian” traffic which is on the wrong VLAN, e.g. frontend traffic injected on the server-to-server network or private addresses from the internet.
Local ports¶
Your application is generally free to use any open port on a machine above 1024. Especially if you run a component that has a registered, well-known port, please use that.
However, custom applications may run into the trouble of colliding with other components. For that we guarantee that the ports 61000-61999 will never be used by our managed components, nor by the kernel when assigning dynamic ports.